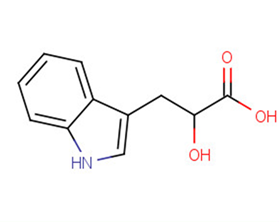
DL-Indole-3-lactic acid
CAS No. 832-97-3
DL-Indole-3-lactic acid( —— )
Catalog No. M20143 CAS No. 832-97-3
DL-Indole-3-lactic acid is a reactant for the preparation of antibacterial agents.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 302 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 447 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 714 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 1017 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDL-Indole-3-lactic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDL-Indole-3-lactic acid is a reactant for the preparation of antibacterial agents.
-
DescriptionDL-Indole-3-lactic acid is a reactant for the preparation of antibacterial agents.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number832-97-3
-
Formula Weight205.21
-
Molecular FormulaC11H11NO3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:10 mM
-
SMILESOC(Cc1c[nH]c2ccccc12)C(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
tri-GalNAc-COOH
Tri-GalNAc-COOH is a ligand for the asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGPR) and is commonly used in lysosomal targeting chimera (LYTAC) investigations.
-
(2-Hydroxypropyl)-β-...
(2-Hydroxypropyl)-β-cyclodextrin is a widely used drug delivery vehicle to improve stability and bioavailability.
-
Oblongine
Oblongine chloride may have potential haemodynamic effects, it can cause a dose-dependent reduction of systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and that these effects are not mediated by α2-adrenergic receptor stimulation.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


